Introduction
The constant demand for aesthetics along with functional restoration has made dental medicine a challenging task. The development of new technologies, materials, and biomechanics has radically changed the approach to replacing dental anatomical structures. In order to offer an optimal solution to this new challenge dental prosthetic restorations using dental zirconia blank with modern 3D multilayering, CAD/CAM modern technology has become indispensable. Dental zirconia blank is among the best material to produce durable and aesthetic dental crowns. Dental Zirconia Blank is the mainstay of most modern dental labs as it provides the solution for a variety of clinical situations including long-span bridges, onlays, veneers, and dental crowns.
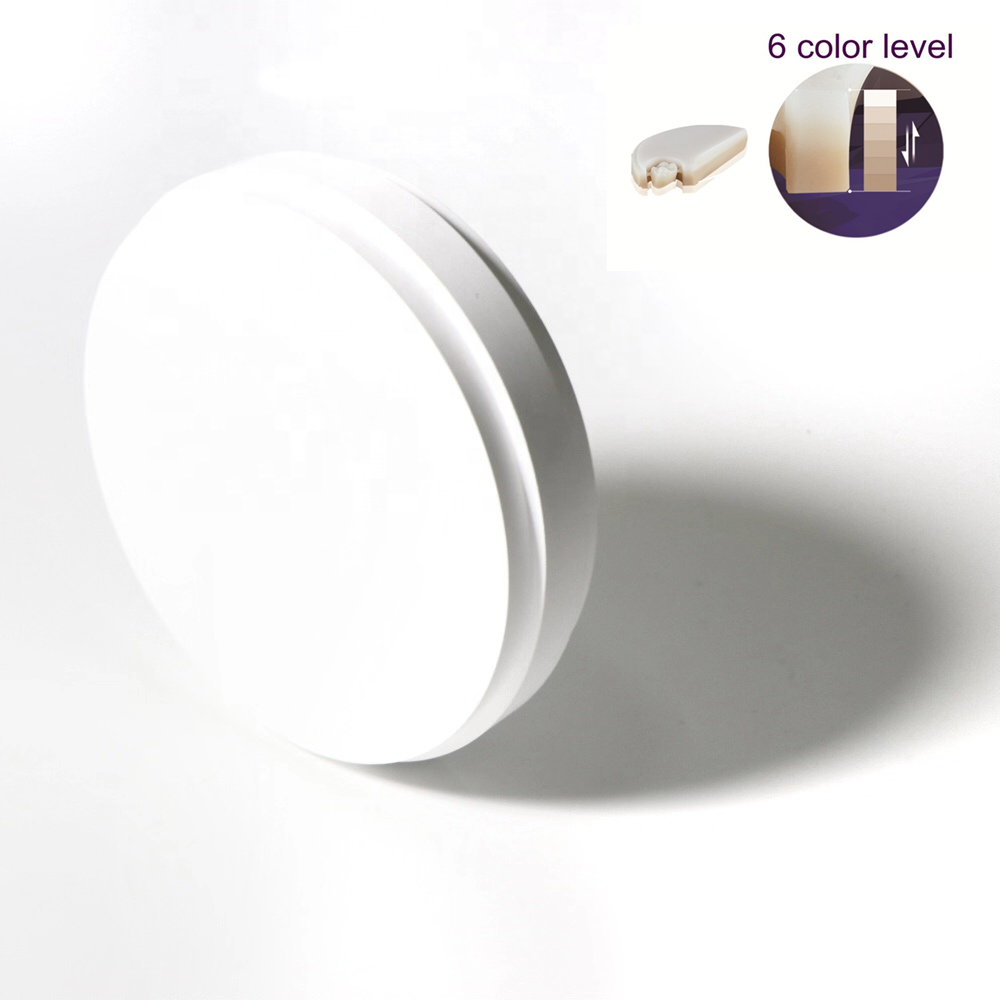

Dental Zirconia Blank: The Material
Zirconium may be a soft, silver-colored metal mined from large deposits in Australia and Africa as a silicate mineral called zircon (ZrSiO4). It had been first isolated in 1824 by Berzelius in impure form. The mineral Zircon is purified to provide zirconia powder with a selected particle size as per dental use. Metal oxides are added to the powder for its geometrical stabilization. Binders and additives are added to the zirconia powder to provide a final dental zirconia blank.
Wear of dental zirconia opposing teeth structure
A number of studies have reported the low wear of dental zirconia blank opposing enamel. The result of that is summarized below:-
- Polished dental zirconia blank wears opposing enamel ten times lower than veneering ceramic wear.
- Wear of the opposing enamel versus dental zirconia blank doesn’t increase with time.
- Glazed dental zirconia blank considerably will increases wear of opposing enamel compared with polished dental zirconia blank.
- The articulating-surface opposing enamel ought to be polished dental zirconia blank.
- Polished denatal zirconia blank wears opposing enamel slightly lower than gold.
Dental Zirconia blank as aesthetic cosmetic
The demand for esthetic restorations has resulted in an argument use of dental Zirconia blank for anterior and posterior restorations. Dental zirconia blank is advocated as the material of selection for matching the natural dentition.
Some decades ago, all-ceramic restorations were restricted to treatment within the anterior region only, but now all-ceramic restorations using dental zirconia blank can be made anywhere in the entire dentition.
In attempts to satisfy the necessities for dental materials and improve strength and toughness, several new ceramic materials and techniques are developed during the past few decades. The flexibility to blend a porcelain crown with its natural counterpart involves consideration of size, shape, surface texture, translucency, and color. The translucency of dental zirconia blank is basically passionate about light scattering. If the bulk of light rays passing through a ceramic is mostly scattered and diffusely reflected, the restoration will appear opaque. If only part of the light rays is scattered and most are diffusely transmitted, the restoration will appear translucent. The number of light rays that are absorbed, reflected, and transmitted depends on the saturation of crystals within the core matrix, their chemical nature, and therefore the size of the particles compared to the incident light wavelength.
Dental ceramic materials exhibit many desirable material properties, including biocompatibility, esthetics, diminished plaque accumulation, low thermal conductivity, abrasion resistance, and color stability. The popularity of dental zirconia blank restorations is basically because of predictable strength achieved with reasonable esthetics.
The use of the zirconium-oxide all-ceramic material provides several advantages, including a high flexural strength (1000 MPa) and desirable optical properties, like shade adaptation to the custom shades and a reduced layer of a thickness (compared to traditional ceramics) of the veneer ceramic required to attain the required color.
- 3D multilayer dental zirconia blank
Recent developments in dental zirconia blank materials finally allow for the use of 3D printed ceramic as materials for patient-specific dentistry. Possible areas of application go beyond classical crowns or bridges and also the use of printed components in applications such as mandibular cages craniomaxillofacial surgery or dental implants. The availability of different ceramic materials allows for applications under load (zirconia) as well as for applications where bone regeneration needs to be induced.
The 3D multilayer dental zirconia for aesthetic feature:
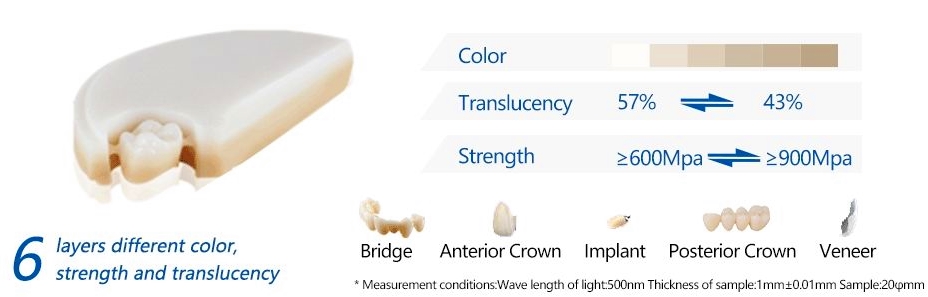
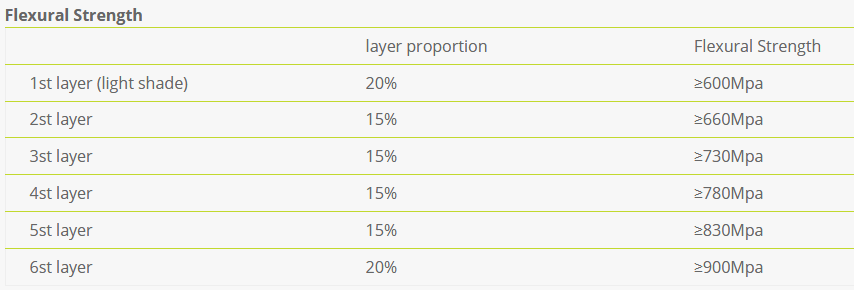
- High Strength: The cervical strength of 3D ziriconia is up to 900MPa for anterior teeth, which is greatly improved.Long span bridges are stable and fully meet the strength requirements of laboratories for a broad range of indications.
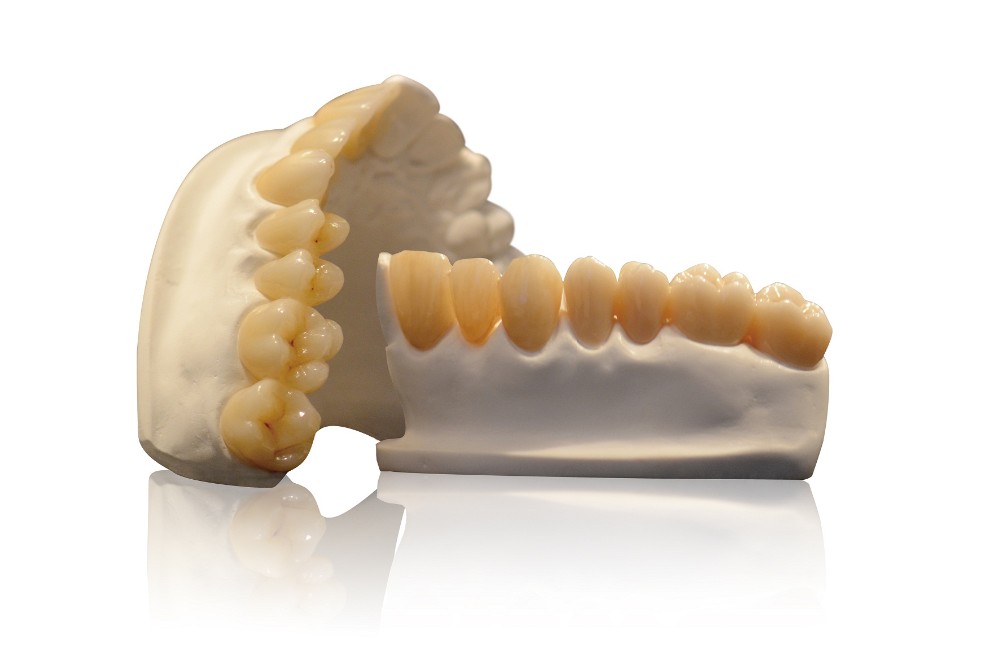
- Layerless Natural Transition: Matching the color transition of natural teeth from cervical to incisal, 3D zironia has a smooth color gradient without visible layer.
- Fast Delivery: 3D zironia is the leading digital solution in the field of Zirconia materials. The excellent characteristics of the material itself, combined with the 3D zironia rapid aesthetic solution will help laboratories to finalize and deliver Zirconia restorations within 24 hours.
Conclusion
Several positive characteristics of dental zirconia blank, like biocompatibility, color, and mechanical properties, make the dental zirconia blank suitable to be used in modern dentistry. However, ceramic bonding, aging, light transmission, and manufacturing processes are all factors that require to be further evaluation so as to guide the successful use of dental zirconia blank as a prosthetic restorative material. Milling dental zirconia blank to full-contour may well be a substitute to traditionally veneered restorations.
The use of dental zirconia blank in modern dentistry has evidently become quite established, with major advancements within the last decade. This could be attributed to its capabilities of meeting all key patient satisfaction criteria (comfort, functionality, social aspects, appearance).
Dental zirconia blank prosthetics are commonly formed and machined from partially sintered blanks, like those produced by CeramTec, thanks to increased reliability and fewer intense machining demands. While there has been extensive research and experimentation on the optimization of key processes like pressing and sintering, there were inevitably visiting knowledge gaps for such a newly realized technology. It’ll be beneficial to CeramTec and to the prosthodontic industry if new and alternative sintering techniques, like two-step sintering, were investigated for their dental zirconia blanks. Experimentation with two-step sintering has shown leads in improving mechanical properties. There is no significant cost increase related to this method compared to conventional sintering, as similar equipment is utilized for both. The target of further investigations would be to optimize key parameters like hardness, flexural strength, and grain growth and size, whilst maintaining the superior aesthetic properties they possess. These may be compared to the results of the prescribed sintering conditions, and to products fully processed from green zirconia powder.
-
 3D ML Zirconia Blocks – All-in-One Dental Restoration Solution with Multilayer Gradient Technology
3D ML Zirconia Blocks – All-in-One Dental Restoration Solution with Multilayer Gradient Technology -
 Fast Sintering Gradient Shade Zirconia Blocks for Aesthetics
Fast Sintering Gradient Shade Zirconia Blocks for Aesthetics -
 3D Pro Multilayer Zirconia Blocks Zircon zahn System
3D Pro Multilayer Zirconia Blocks Zircon zahn System -
 3D Pro Multilayer Amann Girrbach Zirconia Block
3D Pro Multilayer Amann Girrbach Zirconia Block -
 3D Pro Multilayer Dental Zirconia Blocks
3D Pro Multilayer Dental Zirconia Blocks -
 3D multi layer Sirona Inlab Dental Zirconia Block
3D multi layer Sirona Inlab Dental Zirconia Block -
 3D Multilayer Dental Zirconia Disc-Zirkonzahn
3D Multilayer Dental Zirconia Disc-Zirkonzahn -
 3D Multilayer Dental Zirconia Blank-Amann Girrbach
3D Multilayer Dental Zirconia Blank-Amann Girrbach -
 3D Multi layer Dental Zirconia Block
3D Multi layer Dental Zirconia Block
